POST#1

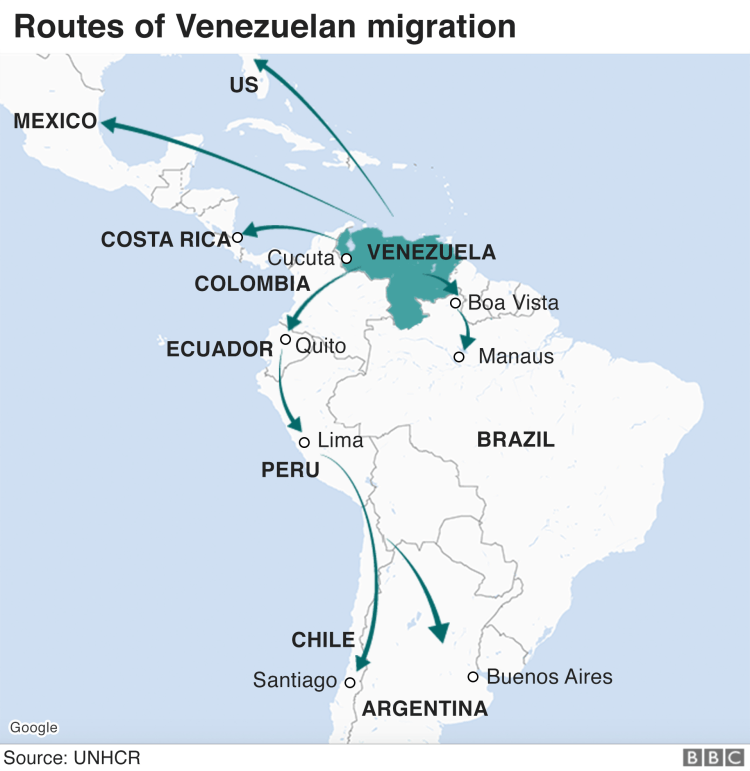
It’s said that the government is using a strategy of instilling fear in its population to retain power. Currently, the president of Venezuela, Nicolas Maduro, has been making changes in the country which have affected thousand of citizens. Venezuelans have opted to migrate to other countries, specially the closest ones, such as Colombia.
The South American country has been caught for years in a political discontent fulled by skyrocketing hyperinflation, power cuts and shortages of food and medicine. Recently, some countries have said that Nicolas Maduro is the legitimate president of Venezuela while other back up Juan Guaido. Juan Guaido declared himself acting president on January 23, 2019, but Nicolas Maduro didn’t accept this, and he condemned as a ploy by the U.S. to oust him. Although, Juan Guaido tried to get the military support, the armed forces remained loyal to President Maduro.
First, Maduro was elected in April, 2013. He was reelected to a second six-year term in May, 2018. Many candidates had been barred from running while others had been jailed or fled the country for fear of being imprisoned, and the opposition parties argued that the poll would be neither free nor fair. Citing articles in the constitution which in such cases call for the leader of the National Assembly to step in, Juan Guaido declared himself acting president.
The National Assembly has continued to meet, but its decisions have been ignored by President Maduro in favour of those made by the National Constituent Assembly. The opposition leader has been further weakened by a corruption scandal involving opposition politicians and by frequent infighting within opposition ranks.
The security forces continue to be seen as the key player in this crisis. They have so far remained loyal to Mr Maduro, who has rewarded them with frequent pay rises and put high-ranking military men in control of key posts and industries. There were talks between the government and the opposition held between May and August, but they didn’t make any progress. As a result, the U.S. has imposed some sanctions on Venezuela, such as freezing on all Venezuelan government assets in the U.S. These type of sanctions had the purpose of weakening President Maduro, so he would drive Maduro out of office, but they failed.
The problems that Venezuela is facing are also results from many years ago due to the presidency of Hugo Chavez who promised to drive down Venezuela’s huge levels of inequality. Former President Chavez took price controls, making goods affordable for the poor. This caused that many Venezuela businesses stopped production because they were no longer making profit. This has been one of the main reasons Venezuela has been economically weak, as well. Currently, people in Venezuela have little to no availability of food to eat. The supermarkets are poorly stocked. There are times in which the electricity is cut. Immigrants in the country were kicked out during Maduro’s presidency. People fight with the militaries, and this has caused many people to die during these confrontations. Venezuela has entered into an absolute despair, which doesn’t seem to be resolved soon.
In the world ranking and fragile state index, Venezuela is a high-warning country in the position 32. The country is expected to again rank as one of the most worsened countries in FSI 2020. Certainly, this performance will likely come as a surprise to few — after all, the country has two presidents claiming legitimacy (and dividing international recognition), the refugee crisis has continued to worsen, the country’s food and health situation has reached a critical point. There is every chance that Venezuela’s FSI score is far from having bottomed-out.
References:
https://www.bbc.com/news/world-latin-america-36319877
https://www.aljazeera.com/news/2019/01/venezuela-crisis-latest-updates-190123205835912.html
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_countries_by_Fragile_States_Index